Niacinamide (also known as nicotinamide and vitamin B3) is a vitamin that applied to the skin can improve wrinkles, tone, redness, excessive sebum, acne…
To make it clear, this post only talks about niacinamide applied topically to the skin and not about niacinamide oral supplementation.
What is niacinamide?
Niacinamide is a water-soluble vitamin that can suit in everybody’s skin due to its multiple benefits that can deal with a multitude of skin conditions.
It is believed that one of the mechanisms by which niacinamide provides skin benefits is that it increases NADP (an electron donor whose NADPH form can regenerate antioxidant systems such as thioredoxins and glutathione).
It has a neutral pH, so irritation chances will be very small and it has the ability to penetrate the human skin.
Niacinamide benefits
It reduces hyperpigmentation and melasma
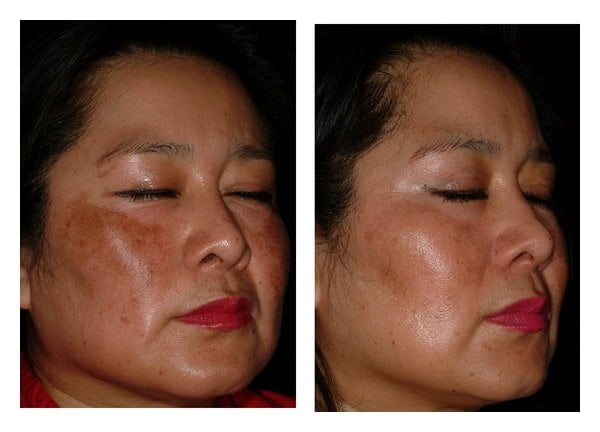
Source: Navarrete-Solís, Josefina et al. 2011 (2011): 379173.
A 2002 study proved that at least a 2% of niacinamide applied to the skin during 4 weeks significantly decreased hyperpigmentation and helped increasing skin lightness due to the fact that niacinamide interferes with the interaction between keratinocytes and melanocytes inhibiting melanogenesis .
Another 2011 study concluded that niacinamide results were comparable to hydroquinone results, as both were able to reduce pigmentation, inflammatory infiltrate, and solar elastosis (Note that when it comes to excellent results hydroquinone is a little more effective).
Deals with acne
A 2017 compilation of studies concluded that 6 of 10 studies showed a significant reduction of acne in patients treated with topical niacinamide. It also concluded that oral nicotinamide may also help with acne.
It helps acne due to its anti-inflammatory properties and its ability to decrease sebum production.
A 1995 study compared the efficacy of 4% nicotinamide gel and 1% clindamycin gel and after 8 weeks the result was that both reduced acne lessons but niacinamide had greater results thank clindamycin.
Improves skin barrier function
Niacinamide is able to improve the stratum corneum (skin barrier) due to the fact that it increased ceramide, free fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis and decreased transepidermal water loss in dry skin imroving its moisture content (2000 study and 2004 study).
Reduces redness and improves skin tone
A 2005 and a 2004 study concluded that just a 5% of niacinamide was able to decrease skin redness. Furthermore it can decrease skin yellowing due to its antioxidant properties that are able to inhibit oxidative processes that produce yellowish-brown color compounds that acumulate in our skin as we age.
It can also helps with rosacea (2005 study) due to niaciname’s properties that help improving skin barrier function.
Decreases oil production
Niacinamide has demostrated that just a 2% of niacinamide lowered sebum production (2006 study) just in 2-4 weeks. It’s thougth that this happens due to the fact that niacinamide reduces triglyceride and fatty acid synthesis (two of the majors sebaceous gland lipid compounds).
Has antiaging effects
Wrinkles, fine lines and elasticity were improved using topical niacinamide (2005 study) as niacinamide increases collagen and other protein types production and can inhibit GAGs (glycosaminoglycans) excess.
Another 2008 study proved that apart of its wrinkle reduction effects, niacinamide if well tolerated and is safe to use in the eye areas.
Niacinamide acts as an antioxidant
A 2019 study claims that niacinamide can protect skin cells from oxidative damage acting as an antioxidant and being able to repair DNA damage.
It works by inhibiting ROS (reactive oxygen species) that can cause oxidation of lipids, protein (such as collagen or elastin) and DNA. Furthermore niacinamide also reduced cell apoptosis (a process in which cells die).
Protects from sun damage
Research shows that niacinamide has photoimmunoprotective effects when is applied to the human skin. Furthermore it has shown photoprotective effects against carcinogenesis in mice.
Another study concluded that niacinamide was able to repair DNA damage induced by UV radiation by reducing photolesions in keratinocytes and other human skin cells.
Reduces pores size
Niacinamide can shrink pores due to the fact that it increases skin elasticity. Furthermore, due to its sebum regulation properties it may make the pores smaller as imperfections decrease.
Niacinamide side effects
Niacinamide is generally safe used in the skin and has minimal possibilities to have side effects, however, everyone’s skin is different so it will be better to do a patch test before applying to the entire face to avoid skin irritation.
Some people are sensitive to niacinamide (specially at high concentrations), even though niacinamide should not cause breakouts if you experience a breakout during the use of a product that has niacinamide it could mean that you’re sensitive to niacinamide.
